Integrated Health Screening for Tuberculosis, Respiratory Diseases, and Cardiovascular Conditions
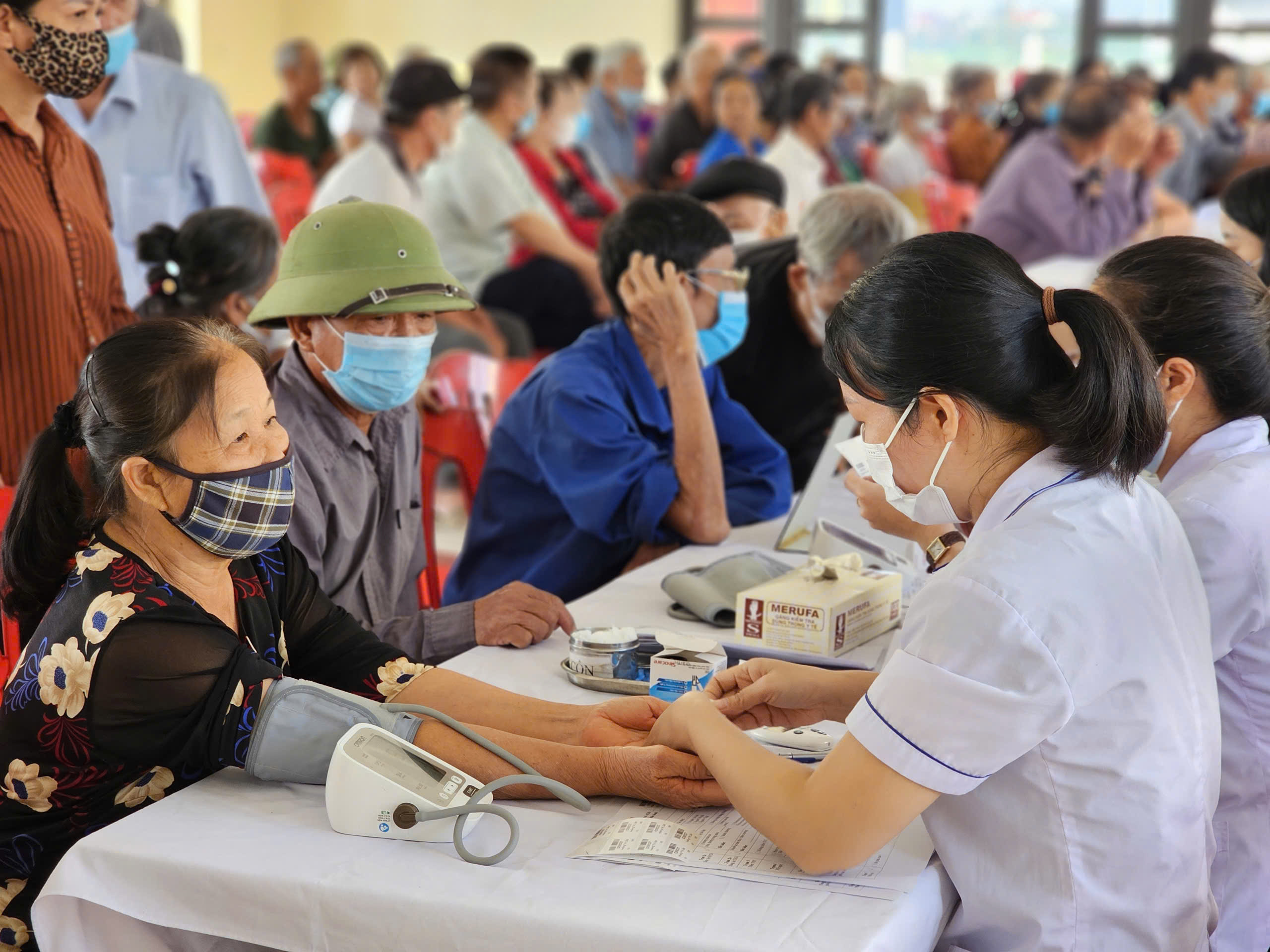
Tuberculosis, chronic respiratory diseases and cardiovascular diseases cause numerous deaths every year.1 2 According to the World Health Organization (WHO), tuberculosis is the deadliest infectious disease with 1.25 million deaths worldwide (2023).3 The United Nations and its member states have committed to ending the global TB epidemic by 2035 as part of the Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs). However, a comprehensive and innovative strategy is urgently needed to make this goal a reality. Supported by the Stop TB Partnership, Global Affairs Canada and the UK’s Foreign, Commonwealth & Development Office, Dr. Eimo Martens, Priv.-Doz. Dr. med. Gregor Zimmermann and Dr. Eva-Maria Brandner (TUM University clinic rechts der Isar) as well as Luan Vo, Andrew Codlin and Huong Mo (Freundeskreis für Internationale Tuberkulosehilfe e.V. (FIT)), cosinuss° and other partners in Vietnam are working on testing, evaluating, and scaling this new, person-centered way of integrating TB prevention and care into primary health care systems. Novel approaches like these could stop TB transmission, reduce suffering from major non-communicable diseases, and ultimately save lives.
Project DISPATCH: Deploying Integrated Services for a Practical Approach to Tuberculosis, Chest and Cardiovascular Health
cosinuss° is participating in Project DISPATCH, an initiative part of Stop TB and aimed at implementing effective Tuberculosis programs in Vietnam. As a key technology partner, our c-med° alpha in-ear sensor will support the screening process by providing continuous and precise monitoring of critical vital signs. This helps to identify and prioritize care and resources for those in greatest need. The collected data will also be used to develop novel integrated screening algorithms designed to recognize early signs of disease.
Advancing Integrated Health Screening with cosinuss°’ Technology
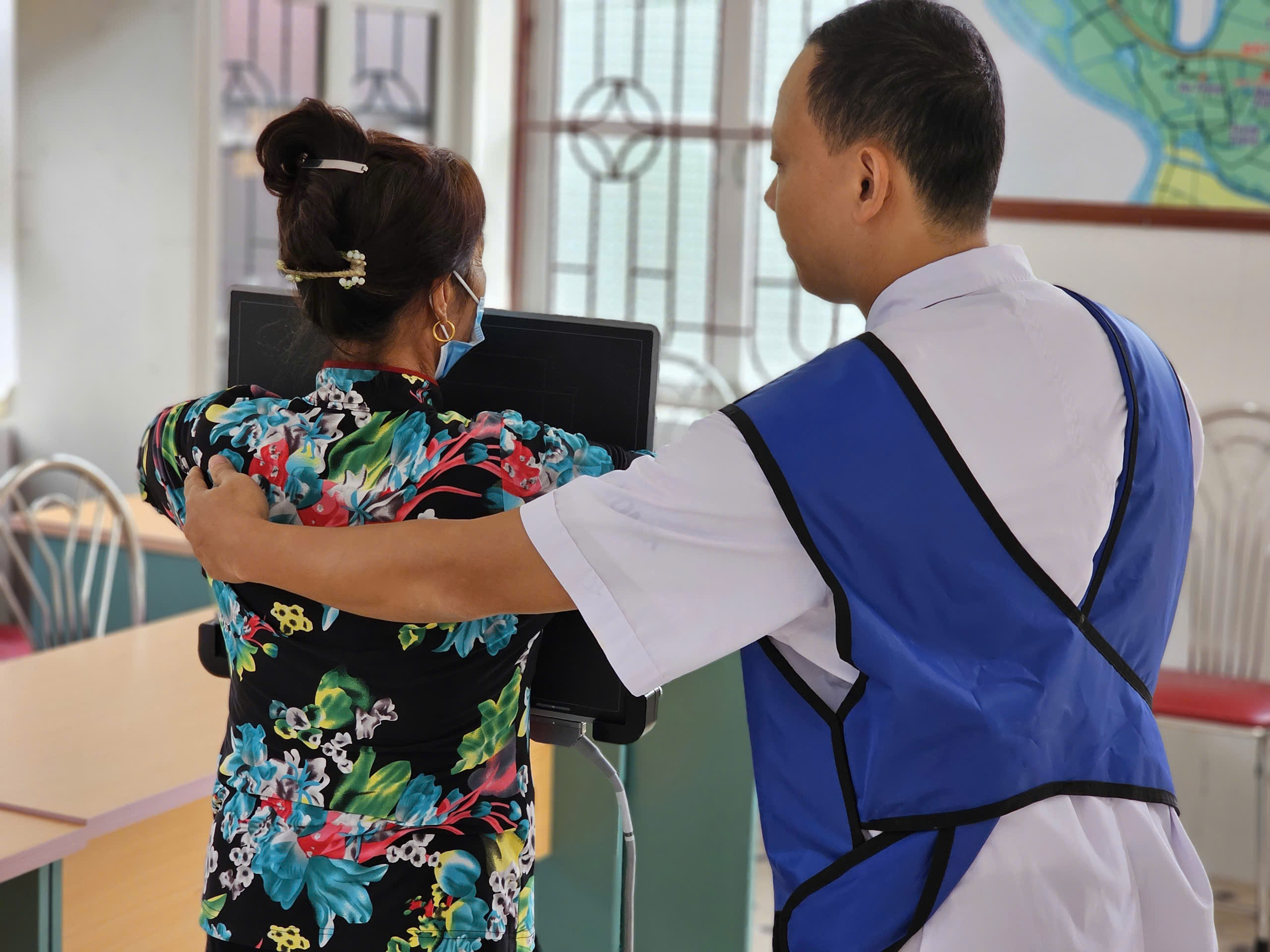
In response to the growing burden of tuberculosis (TB), chronic respiratory diseases (CRD), and cardiovascular diseases (CVD) in urban Vietnam, we are implementing a comprehensive health screening and integrated service delivery (ISD) model. This initiative targets vulnerable populations across five key provinces, using an innovative one-stop shop approach that combines TB diagnostics with early detection of CVD and respiratory diseases. The project aims to screen over 25,000 individuals with advanced diagnostic tools including AI-assisted digital chest X-rays and mobile health technologies. Our goal is to enhance early detection and provide timely treatment, particularly for patients with multiple comorbidities.
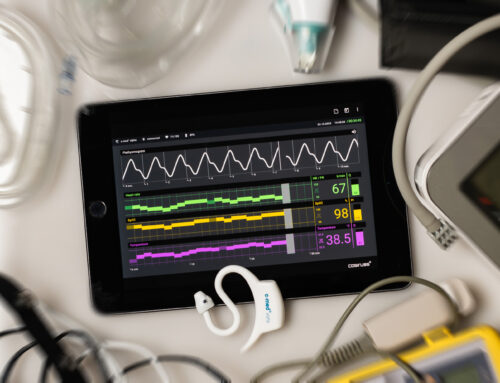
An innovative component of our screening process is a cutting-edge vital sign monitoring system. This system includes an in-ear sensor for pulse oximetry and temperature measurement, continuous blood pressure monitoring, and a 6-channel ECG, all of which provide real-time, high-quality data on participants’ cardiovascular and respiratory health. These devices are essential for identifying at-risk individuals and improving diagnostic accuracy for conditions such as TB, hypertension, atrial fibrillation, and COPD. By seamlessly integrating technology with healthcare services, we can ensure a holistic approach to patient management and prompt referrals for necessary care.
Throughout the project, we plan to collect health data from up to 25,000 participants. Each participant will contribute 15-20 minutes of data covering multiple vital signs and diagnostic measures, including:
- Pulse oximetry, IR thermometer, blood pressure, and ECG
- Vitals data captured at approximately 6 readings per second
- ECG with 6 channels, each sampled at 533 Hz
- PPG (photoplethysmogram) data from pulse oximetry at 3 x 200 Hz
- Accelerometer data with x, y, z axes at 2 x 100 Hz
This high-resolution data—amounting to up to 123 billion data points—will enable precise monitoring of health and provide invaluable insights for managing TB and chronic diseases. By integrating this information into the screening process, we aim to significantly improve diagnostic accuracy and patient outcomes, creating a lasting impact on the population.

Project Goals & Outlook
The project aims to explore the effectiveness of integrated patient services for TB, CRD, and CVD in key vulnerable populations. Through this project, we aim to reduce the burden of undiagnosed and underreported TB while also addressing the rising prevalence of non-communicable diseases like CVD and respiratory conditions. By expanding the scope of the WHO PAL strategy and incorporating AI-assisted surveillance and continuous monitoring, we are paving the way for an integrated, patient-centered model of care that not only treats disease but also empowers patients to take charge of their health. The anticipated outcomes include diagnosing over 350 persons with TB, 5,000 with hypertension, 600 with COPD and overall improved health management through the seamless integration of services across the care continuum.
Stay tuned: cosinuss° will report on the progress of the project and share initial results in the coming months.
Project runtime
The project started in March 2025 and is initially scheduled to run for 18 months.
Project partner
Photo credit: Friends for International TB Relief (FIT)
Quellen / References
- WHO Fact Sheet “Cardiovascular diseases (CVDs)”, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (last call: 17.3.2025)
- WHO Fact Sheet “COPD”, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/chronic-obstructive-pulmonary-disease-(copd) (last call: 17.3.2025)
- WHO Fact Sheet “Tuberculosis”, https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/tuberculosis (last call: 17.3.2025)